Dandruff vs dry scalp both are different conditions in root cause. Lack of moisturization causes dry scalp and excess of oil in the scalp causes dandruff .People want to cure dry scalp flakes vs dandruff without knowing the causes of dandruff and dry scalp. This blog is about helping you to overcome your scalp problem and using methods to overcome them.
Dry scalp causes:
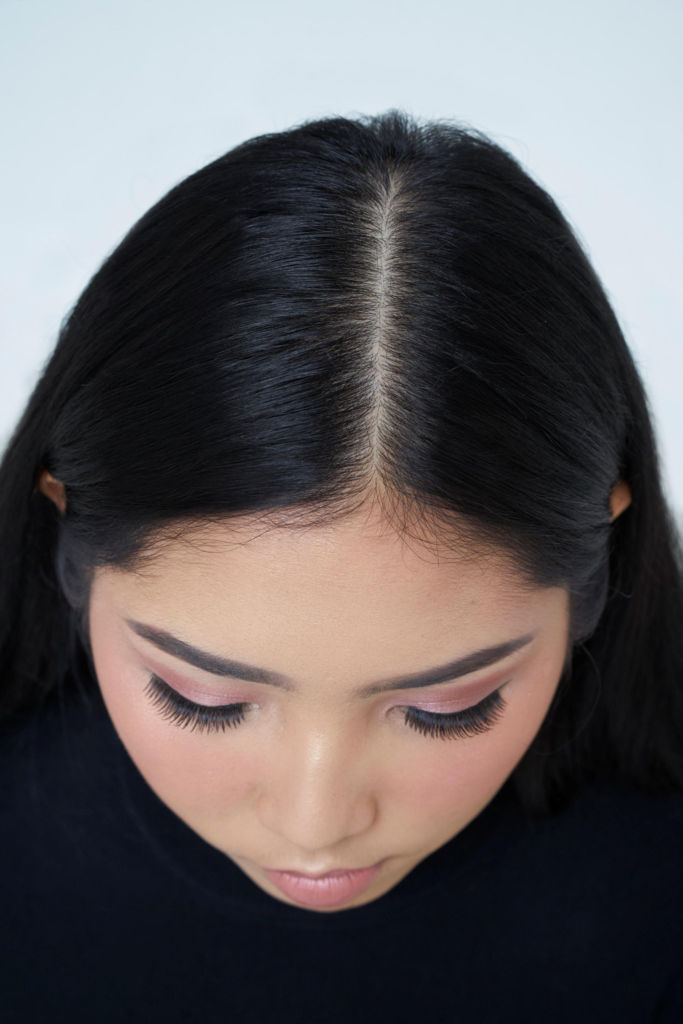

Sebum Production: Sebum is the natural oil the scalp produces to moisturize and protect the skin. Sometimes, the scalp may produce too little sebum, leading to dryness.
Skin Type: Just like other parts of the body, individuals have different skin types. Some people naturally have dry skin, including on their scalp, which can predispose them to dry scalp issues. Some skin conditions also cause dry scalp.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Psoriasis
Fungal Infections
Contact Dermatitis
Age: As people age, the skin produces less oil, leading to drier skin, including the scalp.
Weather: Extreme temperatures, particularly cold and dry weather, can strip moisture from the scalp, leading to dryness and flakiness.
Excessive washing: washing hair more than recommended for the scalp, leading to dryness.
Hair Products: containing harsh chemicals or alcohol, can irritate the scalp and contribute to dryness.
Hair Styling Tools: Excessive use of heat styling tools like hair dryers and straighteners can dry out the scalp by depleting its natural moisture.
Hair Dyes and Chemical Treatments: Chemicals in hair dyes and other treatments can irritate the scalp and cause dryness.
Overuse of Hair Products: Excessive use of styling products like gels, mousses, and hairsprays can build up on the scalp, leading to dryness and flakiness.
Hydration Level : Dehydration, which can affect the skin’s overall health, including the scalp.
Dandruff scalp cause:
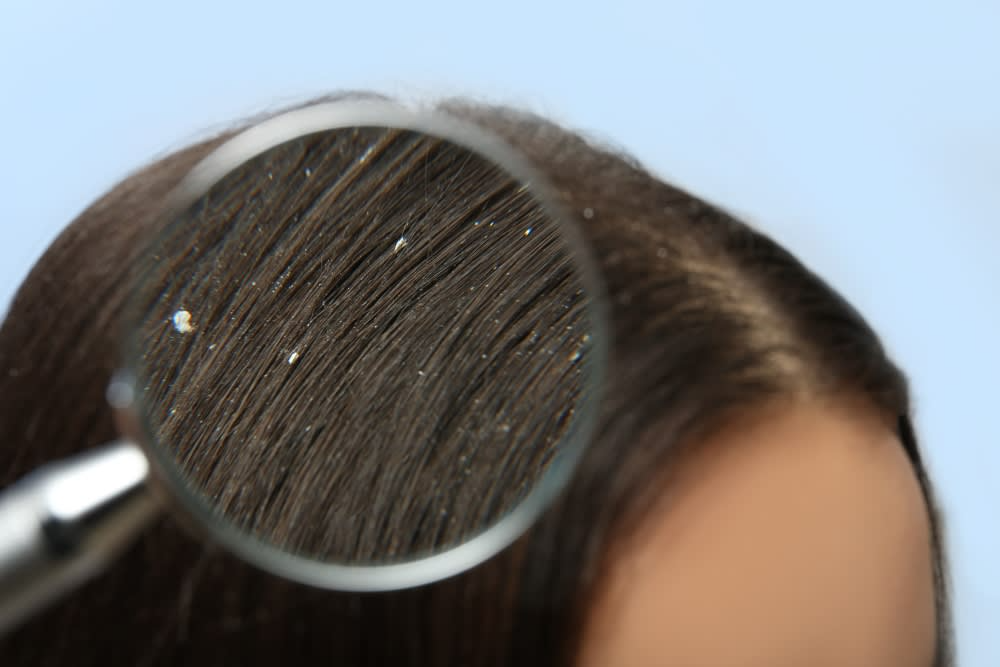

Dandruff is a common Problem. It often presents as flakes in white and yellow.
Malassezia Fungus:
The most common cause of dandruff is a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia. This fungus is naturally found on the scalp of most adults but can overgrow in some individuals, leading to dandruff to scalp that irritating and accelerating the shedding of skin cells.
Seborrheic Dermatitis:
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin covered by flaky white or yellow scales. Combination of factors, including the overgrowth of Malassezia fungus, excessive oil production, and individual susceptibility.
Dry Scalp:
While dry scalp and dandruff are different conditions, they can sometimes overlap. When the flakes are large and dry, they may be mistaken for dandruff. However, dry scalp flakes are typically smaller and less oily than dandruff.
Excessive Oil Production:
Conversely, excessive oil production (seborrhea) can also contribute to dandruff, increasing dandruff production.

Stress and hormonal changes:
Stress and hormonal fluctuations can impact the body’s immune system and oil production, potentially exacerbating dandruff symptoms. Some people may notice an increase in dandruff during periods of high stress or hormonal changes, such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
Poor Hygiene:
Infrequent washing, oil, and dirt, contributing to dandruff.
Hair Care Products:
Certain hair care products, such as shampoos containing harsh chemicals or ingredients that irritate the scalp, can trigger or worsen dandruff symptoms in sensitive individuals.
Dietary Factors:
While the role of diet in dandruff is not fully understood, some research suggests that certain dietary factors, such as excessive consumption of sugar, fats, or dairy products, may contribute to dandruff in susceptible individuals.
Medical Conditions:
HIV/AIDS, can also cause dandruff-like symptoms. It’s essential to differentiate between dandruff and these conditions, as they may require specific treatments.
Symptoms of Dandruff:
White or Yellowish Flakes: Dandruff typically presents as white or yellowish flakes on the scalp and in the hair. These flakes are often larger and more oily than those associated with dry scalp.
Itching: Dandruff is often accompanied by scalp itching, which can range from mild to severe. The itching may worsen when the scalp becomes irritated or inflamed.
Oily Scalp: Dandruff is commonly associated with excessive scalp oiliness due to the overgrowth of the Malassezia fungus. The flakes may stick to the scalp and hair due to the presence of oil.
Redness and Irritation: cause redness and irritation of the scalp, mainly if scratching occurs frequently. This irritation may exacerbate the itching and flaking.
Flakes on Other Areas: Dandruff flakes may not be limited to the scalp alone. They can also appear on other areas with hair, such as the eyebrows, beard, and ears.
Persistent Symptoms: Dandruff symptoms persist over time and may worsen without proper treatment. Individuals with dandruff may notice that the condition recurs periodically, especially during stress or hormonal changes.
Symptoms of Dry Scalp:
Small, White Flakes: Unlike dandruff, dry scalp flakes are typically smaller, lighter in color, and drier in texture. They may appear more like tiny white particles rather than larger, greasy flakes.
Dryness and Tightness: A dry scalp is characterized by tightness and dryness. The skin may feel rough or rough, especially after washing.
Itching: While itching can occur with dandruff and dry scalp, it tends to be less severe. The itching may be mild and intermittent, often alleviated by moisturizing the scalp.
No Oily Residue: Unlike dandruff, a dry scalp is not typically associated with excessive oiliness. Instead, the scalp may appear dry and lacking in natural oils.
Seasonal Variation: Dry scalp symptoms may worsen when the air lacks moisture during dry or cold weather. However, symptoms may improve with proper hydration and moisturization.
Scalp Sensitivity: Individuals with dry scalp may experience increased scalp sensitivity, especially when exposed to harsh hair care products or environmental factors.
Improvement with Moisturization: Unlike dandruff, which requires specific antifungal or medicated treatments, dry scalp symptoms often improve with regular moisturizing therapies, such as using hydrating shampoos, scalp oils, or home remedies like coconut oil or aloe vera gel.
Treatment for the dandruff:
Medicated Shampoos:

Antifungal Shampoos: These shampoos contain active ingredients like to reduce the growth of Malassezia fungus on the scalp.
Tar-Based Shampoos: Shampoos containing coal tar can help on the scalp, reducing flaking and itching.
Salicylic Acid Shampoos: Salicylic acid helps flakiness.
Topical Treatments:
Antifungal Creams or Lotions: In cases of severe dandruff or inflamed scalp, your doctor may prescribe antifungal creams or lotions to apply directly to the scalp.
Corticosteroid Solutions: Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with dandruff. They are available in various forms, including solutions, foams, and sprays.
Anti-itch Creams or Lotions: Over-the-counter anti-itch creams containing ingredients like menthol or hydrocortisone can temporarily relieve the itching associated with dandruff.

Scalp Exfoliation:
Regularly exfoliating the scalp with a gentle scrub will reduce flakiness. It increase removal of the dead skin from skin.
Avoid Triggers:
Identify and avoid triggers exacerbating dandruff symptoms, such as stress, harsh hair care products, and dietary factors.
Lifestyle Changes:
Practicing good scalp hygiene, including regular shampooing and thorough hair rinsing, can help prevent oil buildup and dead skin cells on the scalp.
Treatment for Dry Scalp:
Hydrating Shampoos and Conditioners:

Use gentle, hydrating shampoos and conditioners formulated specifically for dry scalp to help moisturize and nourish the scalp and hair.
Scalp Oils and Moisturizers:
Apply natural oils such as coconut, jojoba, or olive oil to the scalp to moisturize and soothe dryness. Leave the oil on for a few hours, or overnight, before shampooing.
Avoid harmful products:
Avoid harsh products that contain sulfates, alcohol, and fragrances. These substances make your scalp dryer.
Humidifiers:
Use a humidifier in homes to keep air moist in the winter season to prevent further dryness in the head.

Limit Heat Styling:
Reduce the frequency of heat styling tools such as hair dryers, straighteners, and curling irons, as excessive heat can contribute to scalp dryness.
Hydration and Nutrition:
Drinking the recommended amount of water with a balanced diet in minerals, vitamins, and fatty acids helps nourish the body’s over all health and scalp health
Avoid Over-washing:
Limit shampooing to no more than 2-3 times per week to prevent stripping the scalp of its natural oils.
Consult a dermatologist:
If home remedies and over the counter option not treat your dry scalp, Dry scalp symptoms, consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
