Do you have patches of darker skin on your face, arms, or other areas? You might be dealing with hyperpigmentation,and hyperpigmentation cream can help you.
This blog dives deep into understanding hyperpigmentation:
- What it is: We’ll explain what causes hyperpigmentation and its different types, like sun spots, age spots, and melasma.
- Why it happens: You’ll learn about the factors that trigger hyperpigmentation, including sun exposure, hormones, and inflammation.
- How to manage it: We’ll explore various approaches to managing hyperpigmentation, from safe and effective skincare routines to potential professional treatments.
- Embracing your skin: We’ll also discuss self-love and acceptance, emphasizing that hyperpigmentation doesn’t define beauty.
Throughout the blog, we’ll provide reliable information and practical tips to help you navigate hyperpigmentation and feel confident in your skin. Remember, you’re not alone! Join us as we explore this topic together.
What is hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that causes patches of darker skin on various body parts, such as the face, arms, and hands. It can affect people of all skin tones and manifests in different forms, including sun spots, age spots, and melasma. While not harmful, it can cause cosmetic concerns for some individuals.
- Causes of hyperpigmentation
Several factors can trigger hyperpigmentation, leading to the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for our skin color:
1. Sun exposure:
This is the most common cause. When exposed to UV rays, the body naturally produces more melanin to shield itself. Excessive sun exposure can lead to uneven pigmentation, sun spots, and other types of hyperpigmentation.

2. Hormonal changes:
Hormonal Fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause, can stimulate melanin production and cause hyperpigmentation, often appearing as melasma on the face.

3. Skin injuries or inflammation:
When the skin experiences injury or inflammation, like acne, eczema, or insect bites, it can overproduce melanin as part of the healing process, leading to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.

4. Certain medications:
Some medications, including birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, and some antibiotics, can increase sun sensitivity and make individuals more prone to hyperpigmentation.

5. Medical conditions:
Underlying conditions like Addison’s disease, hemochromatosis, and certain vitamin deficiencies can disrupt melanin production and contribute to hyperpigmentation.
It’s important to note that these are general causes, and the specific factors involved in hyperpigmentation can vary depending on individual circumstances. Consulting a dermatologist can help determine the cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Also read this for skin glow;
Treatments
1. Hyperpigmentation creams effects
Here are some potential effects hyperpigmentation creams may have:
- Reduced appearance of dark spots and uneven skin tone: Many hyperpigmentation creams contain ingredients that inhibit melanin production or encourage the breakdown of existing melanin, potentially leading to a more even skin tone and a lighter appearance of dark spots.
- Brighter and more radiant complexion: Some creams also contain antioxidants that can improve overall skin health and promote a brighter, more radiant appearance.
Your dermatologist can also recommend Best Cream for hyperpigmentation, so before using Cream for hyperpigmentation, first consult your dermatologist.

2. Face acids
Face or skin acids are like tiny exfoliators for your skin. They work by gently removing the top layer of dead skin cells, allowing newer, fresher cells to take their place. This process can help even your skin tone and make it smoother overall. Many face acids are readily available at stores like beauty shops and drugstores. Some popular types include alpha hydroxy acids (like glycolic or lactic acid), azelaic acid, kojic acid, salicylic acid, and even vitamin C in its purest form (L-ascorbic acid). In the end we can simply say that it is the best hyperpigmentation skin care.

3. Retinoids
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, are veterans in the skincare world. Their tiny size allows them to dive deep into your skin, working beyond the surface layer (epidermis) to target concerns beneath. You can find over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription retinoid products, but OTC options are usually milder. If you don’t see results after a few months with an OTC product, consult your dermatologist about a stronger prescription retinoid called tretinoin (Retin-A).

4. Chemical peel
Chemical peels use more vital acids to target specific areas of your skin for more profound improvement. They remove the top layer of skin (epidermis) to reduce hyperpigmentation. Even deeper peels can reach the middle layer (dermis) for more dramatic results.
While over-the-counter peels exist, professional-grade peels from a dermatologist are often more robust and deliver faster results. However, due to their potency, these in-office peels also have a higher risk of side effects like redness, irritation, and scarring.
It’s crucial to discuss your risks and concerns with your dermatologist, especially if you spend time in the sun regularly. Chemical peels make your skin more sun-sensitive, so sun exposure after the treatment can worsen hyperpigmentation. Remember, consistent sun protection using sunscreen and other measures is essential for at least a week after your last peel.

5. Laser peel (skin resurfacing)
Laser for hyperpigmentation is a good option. Laser peels, or laser resurfacing, use targeted light beams to tackle hyperpigmentation. There are two main types:
- Ablative lasers: These are stronger and remove layers of skin, offering more dramatic results but potentially causing more side effects.
- Non-ablative lasers: These gentler lasers target the deeper dermis layer to stimulate collagen production, aiming for a tightening effect and improved skin tone.
While both types aim to encourage the growth of new, healthier skin cells, it’s essential to understand that they work differently and have varying potential side effects. Consulting a dermatologist can help you choose the most suitable option for your needs and skin concerns.
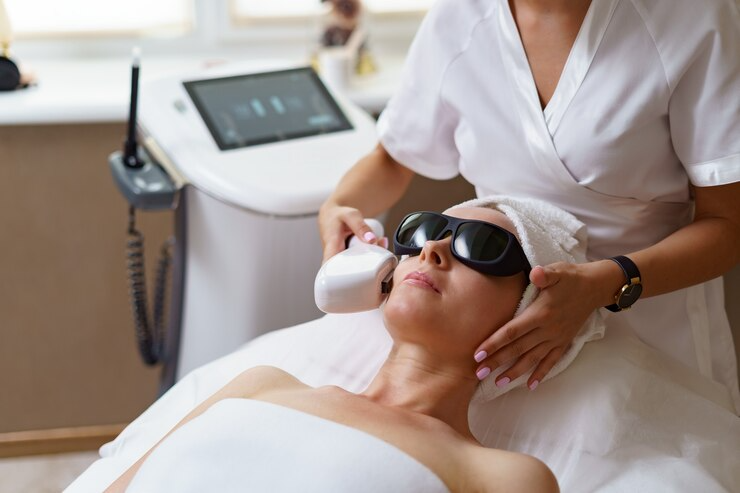
6. Intense pulse light therapy (IPL)
Another non-ablative option is intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, sometimes called a photo facial. Unlike lasers, IPL uses broad bursts of light to stimulate collagen growth within the deeper skin layer (dermis). This treatment usually requires multiple sessions to achieve results. While it primarily targets overall pigmentation concerns and exceptionally flat dark spots, it may also offer additional benefits like reducing the appearance of wrinkles, spider veins, and enlarged pores.
7. Hyperpigmentation soap
HyperpigmentationThe use of soap can also be the solution to skin burns and hyperpigmentation. Many hyperpigmentation soaps are available in the market, which you can use by consulting any skin care specialist.

8. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is an in-office treatment for hyperpigmentation limited to the top layer of your skin (epidermis), often targeting shallow scars. During the procedure, a dermatologist uses a handheld tool with a gentle abrasive attachment to remove the top layer of skin cells. It’s a relatively quick process, but multiple sessions might be required to achieve your desired results.
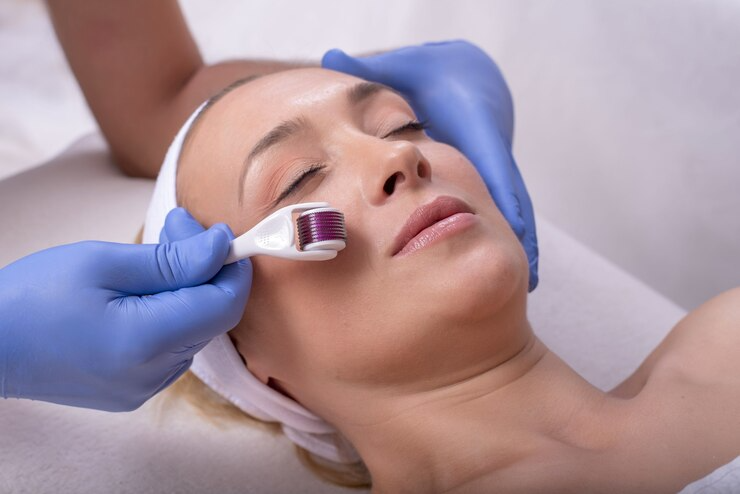
9. Dermabrasion
Unlike microdermabrasion, dermabrasion is an in-office procedure a dermatologist performs to address concerns like acne scars, sun damage, and wrinkles. However, while microdermabrasion only removes the top layer of skin (epidermis), dermabrasion goes deeper, reaching the upper portion of the dermis layer. Both procedures use a handheld tool with an abrasive attachment to gently remove targeted skin layers to promote new cell growth and improve the skin’s appearance. This process might require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
10. Lightening creams
Over-the-counter (OTC) lightening creams offer a convenient option to manage hyperpigmentation. These come as creams or gels and are typically applied once or twice daily to lighten affected areas gradually. Common ingredients in these creams include liquorice extract and vitamin B-3 (niacinamide). While readily available online and in stores, it’s crucial to only purchase from trusted sources. These creams are generally most effective for flat hyperpigmentation like melasma or age spots, working well on various skin tones. Remember, consistency is critical, as results may take time. Consulting a dermatologist can help determine if lightning creams are the best approach for your needs and recommend suitable products.

Dermatologist recommandation
You can use any product, but you must consult with your dermatologist. Dermatologists can give you the best advice and take care of your skin by examining your skin condition. They can tell you the side effects of some products and can make you a skincare routine.

